Major firms like Meta, Microsoft, Google, Apple, and Amazon are pouring resources into immersive platforms after remote work trends spiked post‑COVID. IDC forecasts global spending jumped from about $12B in 2020 to $72.8B by 2024, a clear signal of market momentum.
Augmented reality and virtual reality serve as adjacent pillars that let users access richer, hands‑on experiences. Companies bundle headsets, software, and cloud backbones to deliver collaboration, training, and entertainment tools that feel more natural than flat screens.
Remote work accelerated adoption for enterprise use cases like Meta’s Horizon Workrooms and Microsoft Mesh for Teams. Cloud leaders such as Amazon Web Services and Google support the metaverse frame with infrastructure that scales latency‑sensitive workloads.
This article will map core technologies, firm strategies, advertising models, networks, use cases, and the U.S. outlook. The thesis: the future is not just about devices but about experiences that create real value for users, while privacy, governance, and infrastructure will shape how fast that vision arrives.
Why AR and VR Are Commanding Big Tech’s Attention Right Now
As hybrid work became the norm, firms raced to build immersive tools that let remote teams feel present together. Many users now spend more of their time at home, and they expect richer collaboration than video calls can deliver.
ONS data shows remote work jumped sharply; IDC projects global spending rising from about $12B in 2020 to $72.8B by 2024. Those numbers push the metaverse from concept toward commercial reality. This shift alters the market and speeds adoption as pilots move to scaled use.
Companies view the metaverse as a new computing layer that spans work, play, and social space. Investment targets hardware, content, and networks so that comfort, ease of use, and privacy get solved early.
- Why now: remote habits + clearer business cases for presence;
- Timing matters: early movers shape developer ecosystems and user norms;
- Reality check: success depends on utility and trust.
Smart plays fold immersive tools into existing workflows so teams adopt features where they already work. That practical path helps companies convert curiosity about the metaverse into durable product wins.
AR, VR, and Mixed Reality: Core technologies shaping virtual environments
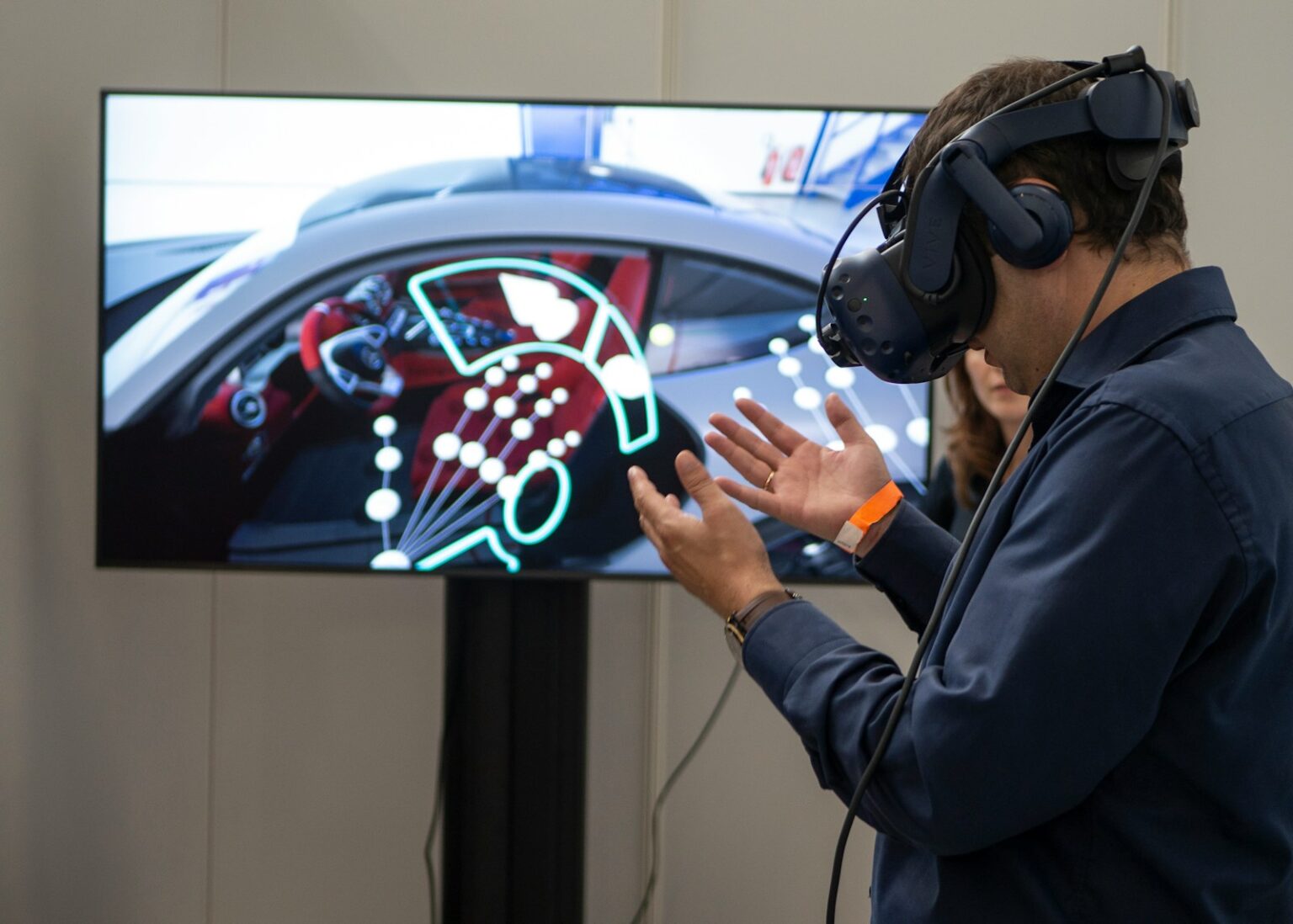
Improved displays and sensors make immersive experiences feel less like demos and more like tools. Virtual reality delivers full immersion through headset-mounted displays. Augmented reality overlays digital elements on the physical world. Mixed reality blends holograms with real objects for interactive scenes.
From immersive virtual worlds to augmented overlays: experience design fundamentals
Experience design rests on a few core elements: rendering fidelity, interaction models, and spatial audio. Hands, controllers, and eye tracking define how users act inside a scene. High-quality audio spatialization and tight sync reduce disorientation and boost presence.
Headsets, glasses, and sensors: hardware performance and user comfort tradeoffs
Hardware choices balance display resolution, refresh rate, optics, weight, and battery life. Sensors—IMUs, depth cameras, and passthrough video—anchor virtual environments to room geometry for stable use. Low latency (motion-to-photon) is crucial to avoid motion sickness during fast motion.
- Performance tactics: foveated rendering, compression, and edge offload help devices push higher fidelity without overheating.
- Ergonomics: lighter frames, adjustable fits, and ventilation extend session length and satisfaction.
- Safety: always-on sensors raise privacy concerns when mapping rooms or recording movement.
| Device | Strength | Tradeoff |
|---|---|---|
| Headsets | High fidelity | Weight, battery |
| Glasses | Comfort, social fit | Limited graphics |
| MR systems | Holographic interaction | Complex sensors |
Early MR exemplars like Microsoft HoloLens show how enterprise holography supports collaboration and training. These technical choices shape content tools and platform standards discussed next.
Market momentum and spending trends in 2025: investment, adoption, and opportunities
Spending trends now show clear momentum. IDC’s data points to rapid growth—global AR/VR spending rose from about $12B in 2020 to $72.8B by 2024. That trajectory gives firms confidence to scale projects and budgets into 2025.
IDC trajectories: what the numbers signal for companies
The rise in spend signals that companies expect returns from hardware, developer tools, and cloud rendering. More capital flows into devices, content studios, and platform tooling. This creates a reinforcing ecosystem that lowers costs for creators and improves quality for users.
Post-pandemic behaviors: time in virtual spaces and use cases
Remote work patterns pushed people to spend more time online—ONS reported 46.6% worked from home at the April 2020 peak, with most favoring hybrid models later. That shift fuels adoption for collaboration, training, and live entertainment.
Environments with low latency and high reliability unlock features like shared holograms and lifelike avatars. Frontier Economics/NIC scenarios show fiber and 5G matter: ambitious innovation needs FTTP long-term, while moderate progress can use FTTC through 2029.
- Addressable market: richer use cases widen enterprise and consumer opportunities.
- Monetization: blended time-on-task shifts session design and revenue models.
- Action: pilot now, stress-test pipelines, and prioritize workflows that beat 2D alternatives.
| Focus | Near-term (2025) | Medium-term (2029) | Key constraint |
|---|---|---|---|
| Devices | Enterprise headsets, premium consumer models | Lower-cost glasses, broader consumer reach | Battery, comfort |
| Cloud & networks | Edge rendering pilots, private cloud for enterprise | Wider 5G/FTTP rollouts for low latency | Fiber and spectrum availability |
| Content & tools | Training, live events, collaboration apps | Mass-market entertainment ecosystems | Developer pipelines, analytics |
How the Big Tech Five are positioning for the metaverse and beyond
Each major player has carved a distinct path toward an immersive future, blending hardware, services, and developer support. These strategies show how devices, cloud scale, media reach, and enterprise tools will shape who wins user attention and business contracts.
Meta
Meta moved from social networks to a metaverse-first posture under mark zuckerberg. It pairs Oculus headsets with Horizon collaboration tools and large R&D budgets. Enterprise deals—like the Accenture purchase of 60,000 units—signal commercial traction and roadmap milestones.
Microsoft
Microsoft targets enterprise mixed reality with HoloLens 2 and Mesh for Teams inside a 250M MAU office footprint. The Activision deal ties gaming IP to platform reach, letting the company blend work tools and immersive games across virtual worlds.
Apple
Apple focuses on comfort, battery, and ecosystem polish. Reports about the N301 mixed reality headset suggest a user-experience first launch that could bring mainstream interest if it balances performance with seamless services.
Google leverages AR wearables history and search strength to own discovery inside virtual spaces. YouTube integrations and interactive video experiments help it shape media and utility inside new environments while learning from past privacy lessons.
Amazon
Amazon plays infrastructure. AWS—about one-third cloud share—supports 3D streaming partners and offers edge via Wavelength for low-latency needs. That backbone helps companies scale graphics-heavy experiences.
- Device-led: Meta, Apple
- Enterprise toolchains: Microsoft
- Discovery & media: Google
- Cloud & edge: Amazon
| Player | Primary vector | Key assets | Milestone signals |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meta | Device + social platform | Oculus, Horizon, supercomputer | Enterprise sales, R&D spend |
| Microsoft | Enterprise MR + gaming | HoloLens 2, Mesh, Activision IP | Corporate integrations, studio releases |
| Apple | User experience | N301 headset, tight ecosystem | Comfort & battery benchmarks |
| Search & media discovery | AR wearables lineage, YouTube | Interactive media features | |
| Amazon | Cloud & edge | AWS, Wavelength, 3D streaming partners | Edge deployments, partner contracts |
Understanding Big Tech’s Investment in AR and VR: strategies, ecosystems, and control
Who makes the operating layer will shape how users discover, pay for, and share virtual content. Mobile offers a clear precedent: platform owners set rules that steer revenue, notifications, and hardware access.
Owning the OS and platform rules: lessons from mobile shaping AR/VR playbooks
Google’s Android deal shows how defensive platform control protects core services and ad reach. Firms now seek similar influence so the metaverse can be monetized and moderated at the system level.
OS rules will determine ad surfaces, sensor access, and permission flows. That control shapes who wins user attention and payment flows.
Tools, content, and data: building sticky experiences for users and developers
Platform strategy blends SDKs, engines, cloud, and first-party content to lower friction for creators. These tools anchor developers and speed app delivery.
- Data pipelines power recommendations and collaboration that keep users returning to reality-anchored sessions.
- Openness vs control: companies tune policies to balance growth, privacy, and reliable monetization.
- Sticky applications: training, support, and design apps become durable when paired with shared identity and cross-device continuity.
| Approach | Developer benefit | Platform risk |
|---|---|---|
| Open | Wide innovation | Harder safety enforcement |
| Controlled | Integrated payments | Less third-party reach |
| Hybrid | Best of both | Complex policy tradeoffs |
To compete, each company should prototype across ecosystems while building its own content and data moat. Cross-device identity, payment integration, and trust will define platform wins in the metaverse era.
Advertising in virtual and augmented reality: monetization models in virtual worlds
Brands will find ad space inside immersive worlds where creative depth meets measurable action. This shift lets storytelling and direct response converge so users can act without leaving an experience.
Brand plus direct response in VR
In headset-based virtual reality, intermission creatives can showcase products, run tutorials, or offer try-before-you-buy demos. For example, an ad break during a drone race can let players test a controller or buy a skin instantly.
Key advantage: conversions occur inside the world, shrinking the path from discovery to purchase.
AR as the contextual canvas
Augmented reality uses place, time, and behavior to surface moment-perfect offers. A curbside AR prompt might show a time-limited discount for a nearby cafe while a commuter passes.
Relevance rises with safety: offers must avoid distracting users during driving or private moments.
Privacy, targeting, and platform governance
OS-level rules will gate targeting, frequency caps, and creative formats. Platforms can require on-device processing, consent flows, and data minimization to keep trust high.
- Tools advertisers need: 3D pipelines, contextual APIs, and measurement that reads gaze and gesture.
- Comfort rules: no jarring overlays, respect personal space, ergonomic interactions.
- Measurement evolution: clicks → spatial interactions, session funnels, and in-experience attribution windows.
| Ad Format | Use Case | Primary Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Intermission VR spot | Product demo during game break | In-experience conversions |
| AR location prompt | Time-limited local offer | Redemptions per foot traffic |
| Try-on 3D commerce | Virtual try-before-you-buy | Purchase rate after trial |
| Spatial sponsorship | Branded environment elements | Engagement time and retention |
Responsible ads can fund richer content and tools while keeping safety and trust central. The metaverse will expand inventory, but platform governance will decide which formats scale.
Networks, latency, and reliability: the digital highway powering AR/VR
High-capacity connectivity and smart edge placement are the unsung enablers of smooth virtual scenes. Very high capacity networks—full fiber (FTTP) and 5G—are foundational for sustained performance in immersive workloads. Policymakers in the EU and other markets now favor VHCN rollout because the economic case for long-term productivity gains is strong.
VHCN, FTTP, and 5G: why very high capacity networks matter for performance
FTTP gives symmetric throughput and stable uplinks that headsets need for volumetric video and cloud rendering. 5G adds mobility and local wireless access. Together they support high concurrency, consistent bitrates, and the heavy data flows modern virtual environments demand.
Ultra-low latency to fight VR sickness: core network and edge compute needs
Motion-to-photon delay links directly to user comfort. Core optimization and edge offload cut round-trip times and reduce jitter. Designs must prioritize deterministic routing, packet prioritization, and edge placement to meet human latency targets.
Reliability at scale: ensuring consistent QoE for consumers and enterprises
Enterprises require near-zero stalls during training or collaboration. Consumers will abandon unreliable sessions. Telco-cloud partnerships, QoS APIs, adaptive streaming, foveated rendering, and robust observability are key tools to preserve quality.
| Network Element | Role | Primary benefit | Key metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| FTTP | Last-mile fiber | Symmetric bandwidth, high reliability | Available throughput (Mbps) |
| 5G (edge) | Wireless access + local edge | Low latency, mobility | RTT (ms) |
| Core transport & peering | Backbone routing | Deterministic paths, low jitter | Jitter & packet loss (%) |
| Edge compute | Rendering & session logic | Reduced motion-to-photon, scale | Edge hop count & response time |
Enterprise and consumer use cases: from remote work to gaming and education
From training floors to concert halls, practical applications are turning immersive platforms into everyday tools.
Workplace tools and collaboration
Avatars, shared whiteboards, and persistent rooms let distributed teams feel present. Persistent spaces reduce setup time and cut meeting fatigue by keeping context between sessions.
Examples: holographic calls for field crews, Mesh-style collaboration for design reviews, and Accenture’s bulk headset buys for scaled training.
Mixed reality training
Mixed reality can overlay step-by-step guidance on physical equipment. That improves safety, shortens onboarding, and boosts retention for technical tasks.
Healthcare and industrial firms use simulated practice to rehearse procedures before real-world use, reducing errors.
Gaming, entertainment, and virtual economies
Gaming drives engagement and funds creative toolchains that cross into virtual worlds. Live concerts, sports, and shared events add proximity, chat, and collectible drops.
These formats spawn new content models and community behaviors that companies can monetize responsibly.
Commerce, education, and applications
AR try-ons and 3D product models help consumers preview purchases at home, lowering returns and raising confidence.
Education benefits from virtual field trips and simulated labs. Surgical rehearsal and remote mentoring show clear gains for clinics and schools.
- Integration wins: linking tools, identity, and payments smooth workflows.
- Accessibility: ergonomics and assistive features keep sessions comfortable for consumers.
- Governance: privacy and compliance matter most for classrooms, clinics, and regulated sectors.
Early adopters capture learning curves, refine pipelines, and help shape platform road maps. For practical enterprise use cases, see an overview of augmented reality for business use cases.
Outlook for the United States: adoption drivers, constraints, and competitive dynamics
U.S. rollout speed will decide whether immersive platforms become everyday tools or remain niche experiments. Fast fiber and targeted subsidies can widen opportunity across regions. Policymakers and companies must coordinate to avoid a digital divide that locks out rural users.
Infrastructure rollouts, affordability, and the risk of a digital divide
Affordability programs plus FTTP and 5G build-outs lower barriers for homes and businesses. Without incentives for last‑mile builds, many communities will lag.
Performance, content ecosystems, and consumer readiness shaping timelines
Adoption ties directly to latency, symmetric bandwidth, and device prices. Rich content and retail support speed consumer uptake. Firms should stage pilots, regional rollouts, and feedback loops to refine offerings.
- Competitive dynamic: partnerships between cloud providers, carriers, and device makers shape regional QoE.
- Risk: rural and underserved areas need subsidies and build incentives.
- Tip: augmented reality features can add value on current phones while headsets mature.
| Factor | Near-term impact | Policy action |
|---|---|---|
| FTTP/5G | Better reliability, lower latency | Targeted subsidies, streamlined permits |
| Device cost | Limits consumer reach | Tax credits, retail financing |
| Content & services | Drives purchase decisions | Support developer grants, standards |
Measure progress with dashboards that track market adoption, QoE, user satisfaction, and learning or productivity gains to align policy with the long‑term vision for the metaverse.
Conclusion
The metaverse is moving from experiment to everyday tools as platforms, studios, and networks align to deliver richer experiences for work, play, and social life. This vision depends on steady development across devices and cloud pipelines so users get useful features, not just demos.
Hardware — from comfortable headsets to lightweight glasses — must meet design and battery goals while cloud and edge services guarantee low latency. Platform control, content pipelines, and developer tools will shape how fast that development scales, and how good the user experience feels.
Gaming DNA and live games seed communities, monetization, and design patterns that other applications can adopt. Companies should prototype with multiple players, invest in 3D pipelines, and plan network‑aware experiences. Trust — privacy, safety, and control — will decide adoption at home and at work.
Pragmatic outlook: the space is early but momentum is clear; those who learn now will help set standards for the virtual worlds of the near future.
FAQ
What motivates major tech firms to pour resources into augmented and virtual reality now?
Leading companies see AR and VR as pathways to new platforms for social interaction, work, entertainment, and commerce. Advances in displays, sensors, chips, and cloud networking make richer experiences feasible. Firms expect recurring revenue from hardware, software ecosystems, services, and advertising inside immersive environments.
How do AR, VR, and mixed reality differ in how users experience virtual environments?
Virtual reality fully immerses users in a digital scene via headsets, while augmented reality overlays digital content onto the real world through glasses or phones. Mixed reality blends both, letting virtual and physical elements interact. Each approach demands distinct design rules for presence, input, and safety.
What tradeoffs do manufacturers face when designing headsets, glasses, and sensors?
Designers balance weight, battery life, field of view, display quality, and thermal limits. Lighter, more comfortable devices often mean compromises in battery and compute power. Higher-resolution optics and faster tracking improve immersion but raise costs and heat, so makers tune hardware for target use—gaming, enterprise, or all-day wear.
What do current market trends in 2025 say about adoption and investment opportunities?
Spending continues to rise across hardware, software, and cloud services. Enterprise adoption for training and remote collaboration is strong, while consumer growth depends on compelling content and more affordable headsets. Investors look to platforms, cloud infrastructure, and content studios that can scale audiences and monetization.
How do IDC projections shape strategic decisions by technology companies?
IDC forecasts of AR/VR spending help vendors prioritize R&D, partnerships, and go-to-market plans. Rising enterprise budgets push companies to integrate mixed reality with productivity suites, while consumer forecasts drive investments in gaming, social platforms, and advertising formats.
How did post-pandemic behavior influence time spent in virtual spaces?
Remote work and virtual events accelerated demand for collaboration tools and shared virtual venues. Users became more comfortable with remote presence, increasing interest in persistent social and workspaces. That shift nudged companies to invest in features that replicate informal, serendipitous interactions.
How are the five biggest tech companies positioning themselves for the metaverse?
Meta focuses on social platforms, Oculus/Quest headsets, and Horizon as a social layer. Microsoft targets enterprise mixed reality with Mesh, Teams integrations, and gaming via Xbox and Activision assets. Apple pursues a premium mixed reality headset with tight hardware-software integration. Google leverages AR experiences, search, and YouTube for discovery. Amazon builds cloud and edge services through AWS to support large-scale immersive apps.
Why is owning the operating system and platform rules important for AR/VR ecosystems?
Controlling the OS and developer platform lets companies set standards for app distribution, monetization, and data access—just as mobile shaped app economies. Platform owners can create incentives for developers, enforce privacy rules, and capture a larger share of revenue from services and advertising.
What roles do tools, content, and data play in creating sticky AR/VR experiences?
Development tools lower barriers for creators, while high-quality content attracts users. Data—about interactions, preferences, and locations—helps personalize experiences and ad targeting. Together they form a feedback loop: better tools produce richer content, which draws users and generates data to refine the platform.
How will advertising and monetization work inside virtual and augmented worlds?
Models include branded environments, native product placements, contextual ads tied to location or activity, and direct-response formats inside experiences. Brands can create immersive campaigns, while platforms experiment with subscription bundles, revenue shares, and commerce integrations.
What privacy and governance challenges arise with immersive advertising?
Immersive ads can use sensitive signals—eye tracking, gestures, or precise location—raising consent and profiling risks. Platforms must set clear rules for data collection, targeting, and user controls to avoid misuse and regulatory backlash.
Why do networks like 5G and fiber matter for AR/VR performance?
High-capacity networks lower latency and increase bandwidth, enabling richer streaming, multi-user presence, and offloaded compute to the cloud or edge. Without sufficient capacity, users see lag, lower-quality visuals, and higher motion sickness risk.
What is ultra-low latency’s role in preventing VR sickness?
Fast round-trip timing between sensors, compute, and displays keeps visuals synced with head motion. Reducing latency—through edge computing, optimized pipelines, and efficient codecs—helps maintain presence and reduces discomfort for users.
How do companies ensure reliable quality of experience (QoE) at scale?
Firms use redundant networks, edge infrastructure, adaptive bitrate streaming, and performance monitoring to keep experiences smooth. Enterprise deployments add SLAs, private networking options, and managed services to guarantee consistency for business use.
What are the leading enterprise and consumer use cases for immersive tech?
Enterprises use mixed reality for remote assistance, training, design reviews, and hybrid meetings. Consumers gravitate to gaming, live events, social hangouts, education, and AR shopping try-ons. Each sector emphasizes different metrics—productivity for business, engagement for consumers.
How is commerce evolving with 3D product models and real-world overlays?
Retailers deploy 3D models for virtual try-ons, AR previews of furniture, and interactive ads that let users inspect items in context. These features reduce returns, boost conversion, and open new creative ad formats tied to inventory and shopping intent.
What factors will shape adoption across the United States?
Infrastructure rollouts, device affordability, content variety, and digital literacy all influence adoption. Rural broadband gaps and cost barriers risk a digital divide, while strong urban network builds and enterprise demand will drive regional concentrations of use.
What timeline should consumers and businesses expect for mainstream readiness?
Progress is incremental. Expect enterprise solutions and niche consumer hits sooner, with broader consumer adoption hinging on lighter, cheaper headsets and killer content. Infrastructure and ecosystem maturity will likely unfold over several more years.